Forecast Accuracy: The Ultimate Guide from Data to Decisions
Unlock the power of precise forecasting with our comprehensive guide, crafted to transform your inventory management. Designed just for you, we’re offering practical, actionable steps to measure, interpret, and improve forecast accuracy metrics (FAMs). These aren't just theoretical concepts; they are real-world strategies from the Manhattan Active® Supply Chain Planning team that you can implement immediately to see tangible improvements in your day-to-day operations. Get ready to elevate your forecasting game and drive your company’s success to new heights!
Forecast Accuracy: The Ultimate Guide from Data to Decisions
Crack the Code: What’s Forecast Accuracy?
Forecast Accuracy is the precision with which your forecast aligns with actual demand. The closer the match, the higher the accuracy, minimizing deviations.
Achieving higher forecast accuracy isn’t just a goal—it's a game-changer. It’s the cornerstone of reducing inventory, lowering carrying costs, minimizing waste, optimizing resource utilization, and enhancing service levels. Imagine the transformative impact you can create by honing your forecasting skills: streamlined operations, significant cost savings, and elevated customer satisfaction. As an inventory manager, your expertise in enhancing forecast accuracy is pivotal in driving your company’s success and competitive edge.
What’s Bias?
In the world of forecasting, bias is like a sneaky saboteur. It’s a consistent tendency for forecasts to either overshoot or undershoot actual values. If your system or forecaster habitually predicts numbers higher or lower than reality, you've got a bias problem on your hands. Ignoring this can lead to flawed decision-making and planning, wreaking havoc on your inventory management.
High-level steps to enhance forecast accuracy and reduce bias:
- Digging Deep: Unearthing Your SKU Demand History: Dive deep into past data to build a robust foundation.
- Polishing the Past: Treating Your Demand History with Care: Clean and refine your data for accuracy.
- ABC, Easy as 1-2-3: Prioritize Like a Pro with ABC Analysis: Prioritize your efforts where they matter most.
- Measure to Manage: Classify and Conquer Your SKUs: Set clear parameters for analysis and action.
- Set the Bar: Establishing Your Forecast Accuracy Baseline: Establish a reference point to measure progress.
- Measure Up: Selecting the Right FAMs for Forecast Success: Choose the right metrics and timing for assessment.
- Dashboard Delights: Visualizing Your Forecast Accuracy Metrics: Visualize your data to track and communicate performance.
- Celebrate Success: Rewarding Top Forecasters for Stellar Performance: Recognize and incentivize exceptional performance.
- Learn and Improve: Setting Goals and Applying Lessons for Better Forecasts: Continuously refine your strategies and aim for achievable targets.
- Adding Value: Enhance Your Forecasting with VAS: Enhance your forecasting process with additional insights and tools.
Step 1: Digging Deep: Unearthing Your SKU Demand History
Let’s look at each step more closely.
Step 1: Digging Deep: Unearthing Your SKU Demand History
As an inventory manager, you're the key to transforming vast data into valuable insights. Accurate forecasting hinges on having a detailed demand history for your SKUs. But remember, shipment history and demand history are not the same. While shipment records provide useful data, they don’t capture the full picture of demand dynamics.
To build a robust demand history for SKUs, go beyond shipment data. Incorporate information on lost sales and promotional activities to enrich your analysis and offer a more nuanced understanding of demand patterns. Capture demand history at the most granular level possible—monthly, weekly, or daily. Pay special attention to products that replace older ones, and don’t overlook the impact of product returns. Adjust your original demand data for periods with sales influenced by returns. Exclude intra inventory movement between your locations as demand. Aim for a minimum of two years of demand history to establish meaningful seasonal patterns, the more years of historical data the better. Take what you have and enhance it to create an impeccable demand history.
Step 2: Polishing the Past: Treating Your Demand History with Care
This step is all about fine-tuning your data. Accurately depict demand by meticulously analyzing SKU demand history. The general process involves identifying and removing outliers and recognizing and addressing non-repeatable demand patterns, but a sophisticated application offers unparalleled capabilities, including:
- SKU Categorization: Identify and group demand patterns.
- Outlier Management: Handle non-recurring outliers effectively.
- Smoothing Demand Spikes: Manage and smooth nonrecurring demand spikes, especially those influenced by shifting holidays.
Promo Quantity Reevaluation: Adjust promotional quantities for better accuracy.
Refining demand history enhances the quality of seasonal profiles generated at various levels, improving future forecasts for SKUs.
Step 3: ABC, Easy as 1-2-3: Prioritize Like a Pro with ABC Analysis
Reviewing the forecast for every SKU is impractical with a high volume to manage. Efficiency is key. Use the Pareto principle to segment SKUs into ABC classifications. If your expected future forecast aligns with its demand history, classify SKUs according to their historical demand in units, dollars, or both. If not, classify SKUs based on future forecasts. Utilize horizon days for ABC classification to set the timeframe when using future forecast values.
With these segments, a SKU classified as A is more important than one classified as B or C. Run this classification periodically based on your business needs—perhaps quarterly.
According to your business scenarios, introduce a secondary dimension for further segmenting SKUs into XYZ classifications, utilizing historical forecasts and sales data. This may include factors like frequency of demand, demand variation, profit margins, costs, service levels, or other relevant metrics. For example, if you classify based on the frequency of demand, a SKU classified as X has a more stable frequency than one classified as Y or Z.
Form a two-dimensional matrix with the ABC (based on expected demand volume) and XYZ (based on demand variance) classifications.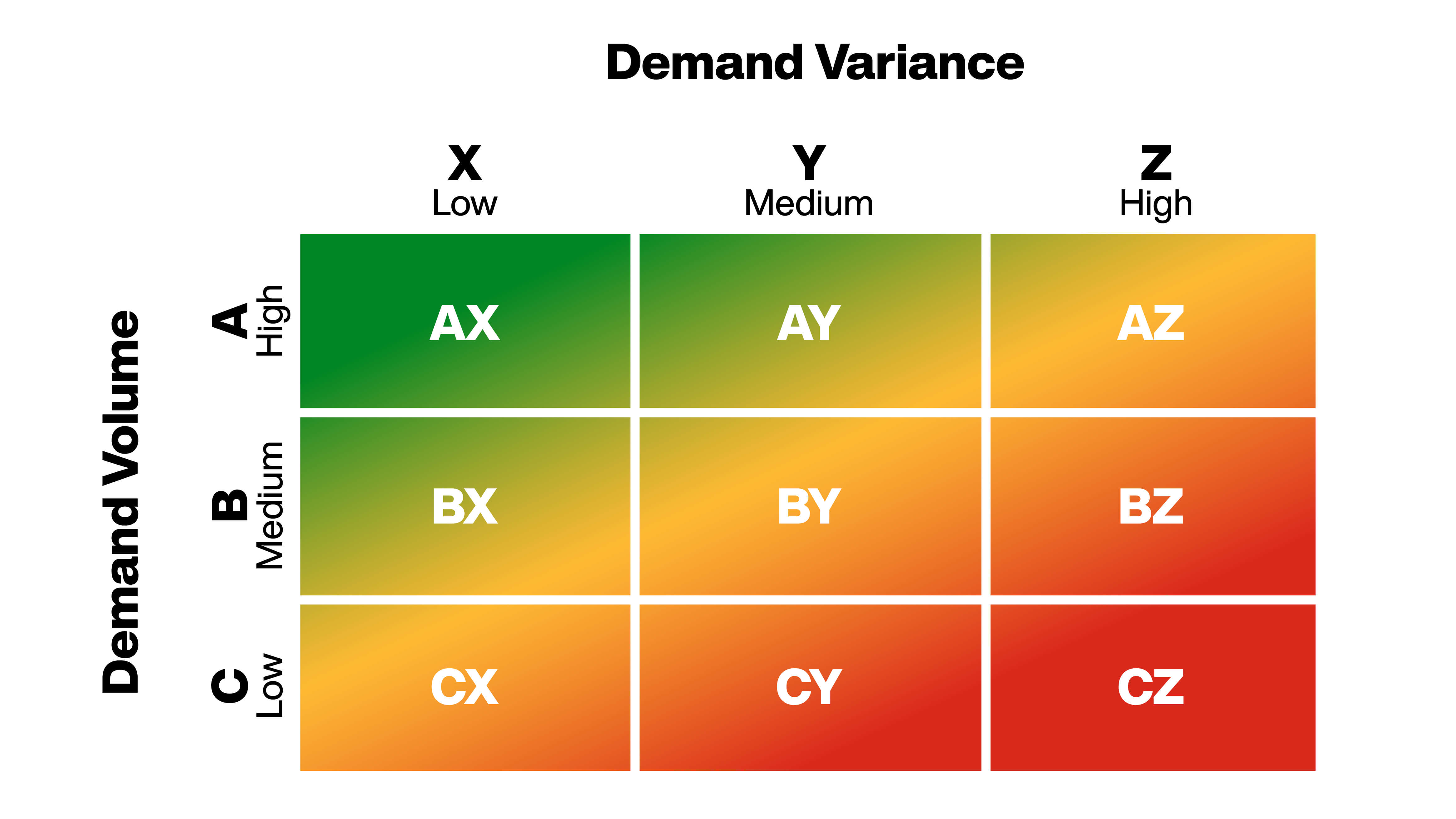
By following these steps, you can focus on the most critical SKUs and make a significant impact on your company's mission. Prioritizing SKUs with higher variability will help you address apparent issues, thereby improving forecast accuracy and positively impacting your company's baseline.
Step 4: Measure to Manage: Classify and Conquer Your SKUs
Time to roll up your sleeves and classify your items! Use your keen judgment to sort your SKUs into three broad categories:
- Easily Predictable: Forecasting these items requires minimal effort.
- Manageable with Effort: These items need reasonable time and attention.
- Unmanageable: Due to high demand variability, these items are tough to forecast accurately at the SKU level.
Instead of struggling with unmanageable SKUs, identify and measure forecast accuracy at a level where the demand pattern is sizable, measurable, and predictable. The key is to determine the right aggregation level to make informed decisions.
For these SKU categories, apply different strategies to maintain enough inventory for when those sales do occur. Sometimes, determining the right level of measurement can be challenging. To tackle this, measure accuracy at multiple levels of product and location hierarchy combinations.
Consider adopting tailored forecast strategies based on SKU categories. For instance, apply a tighter forecast error tolerance for high-velocity items than for low-velocity ones. Similarly, forecasting new SKUs is tricky, but by isolating new products and applying specific forecasting strategies, you'll get the results you need. Using different strategies based on SKU classification will lead to more effective forecasting and better revenue management.
Step 5: Set the Bar: Establishing Your Forecast Accuracy Baseline
Having a point of reference is crucial when measuring forecast performance. It helps evaluate how well a forecaster or the application manages the forecast over time. This point-of-reference forecast doesn’t need to be complicated. For instance, historical forecasts can form a baseline to measure and compare current SKU forecast accuracy metrics. If historical forecasts are unavailable, a simple three-point moving average can be used. Choose any method that’s easy to calculate and present as a baseline.
Step 6: Measure Up: Selecting the Right FAMs for Forecast Success
"What gets measured gets managed." There are many forecast accuracy metrics available, each with its merits and demerits:
- MAPE (Mean Absolute Percentage Error): Great for understanding the magnitude of forecast errors but struggles with zero-demand periods.
- SMAPE (Symmetric Mean Absolute Percentage Error): Provides a balanced view of accuracy and handles zero values effectively. It’s excellent for varying data scales.
- WMAPE (Weighted Mean Absolute Percentage Error): Assigns appropriate weights to critical products or periods, reflecting business priorities. This approach ensures the evaluation of forecast accuracy mirrors specific business goals.
When evaluating forecast accuracy, you might use MAPE or SMAPE for SKU-level granularity, while WMAPE could be beneficial for aggregated (group) accuracy measurement.
SMAPE stands out among forecast accuracy measures. The lower the SMAPE value, the better the forecast accuracy. Forecast accuracy can be defined as 1-SMAPE, giving you the percentage of accuracy.
Feel free to use other metrics like RMSE, MAD, or SRMSE if they suit your needs better. For a metric to be impactful, its results should be easily understandable and interpretable.
Guidelines for capturing forecast accuracy metrics:
- Express forecast error in units, dollars, and percentages (relative error). In some situations, measuring error or improvement in dollars or units provides better insights than percentages.
- Capture the bias to understand tendencies to over or under-forecast, which helps measure precision.
- When deriving consensus, consider both accuracy and bias.
- Comparing current period demand with the forecast doesn’t make sense. Apply the lag/offset, usually the lead time, when measuring forecast accuracy.
- Quantify the cost of forecast errors on both sides (over- and under-forecasting) above agreed thresholds.
- Don't limit your analysis to the forecast accuracy of the current period, but also consider rolling periods. Sample report is below
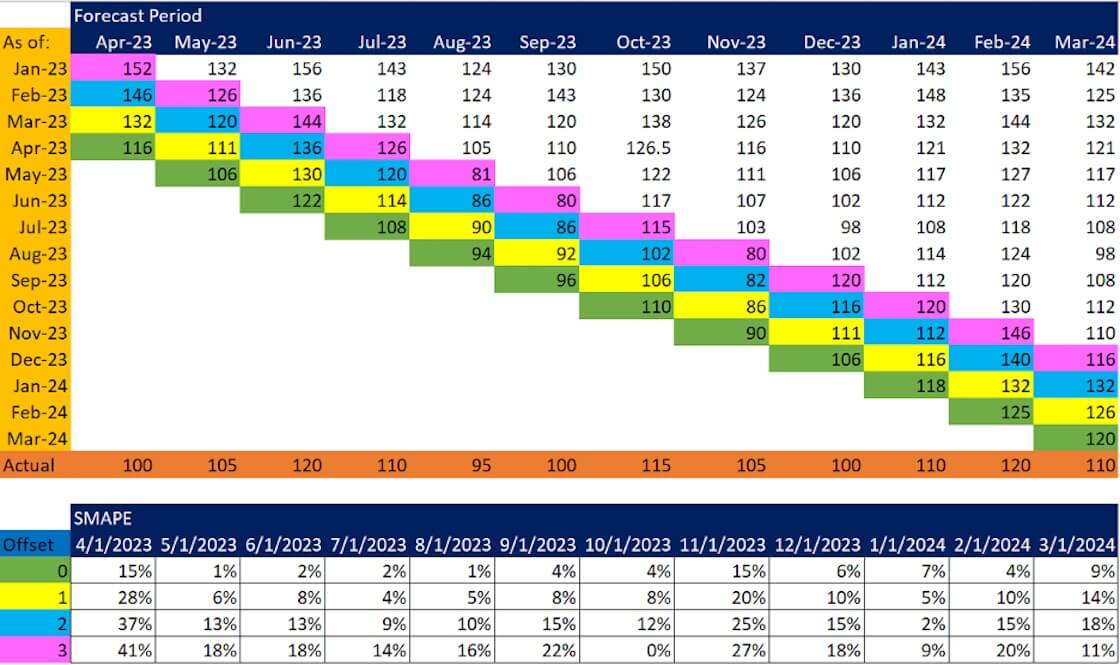
Step 7: Dashboard Delights: Visualizing Your Forecast Accuracy Metrics
It’s time to keep score! Creating a dashboard with Forecast Accuracy Metrics (FAMs) is essential. Focus on the items with the least accurate forecasts to uncover the root causes of errors. Publish your forecast accuracy results regularly. Track the time-phased progress numbers in a table and provide a progress graph.
When publishing forecast metrics, distinguish between system-generated forecasts and those with manual intervention. This clarity ensures transparency in evaluating the accuracy and reliability of your forecasting process. Report overall accuracy and the accuracy of each forecaster. This simple step can have a profound impact on your forecasting process. Healthy competition pushes everyone to improve. Regularly analyzing and communicating forecast accuracy results will elevate the priority of forecasting and improve accuracy over time. Use relevant visualizations to depict forecast accuracy metrics across appropriate horizon days and effectively communicate your business narrative.
Step 8: Celebrate Success: Rewarding Top Forecasters for Stellar Performance
Forecasting can often be a thankless job, so it’s crucial to acknowledge and reward those who excel. Recognize buyers or forecasters who consistently surpass the system forecast. Base rewards on the degree of forecast improvement rather than achieving a specific forecast accuracy number. This motivates them to leverage their product knowledge, customer management skills, and marketing insights to improve system-generated forecasts.
Incorporate the principles of accuracy, completeness, and timeliness into your incentive program. Remember, the farther into the future you forecast, the less accurate it is likely to be. A demand planner managing SKU forecasts may know many things that software doesn’t. Rely on the software forecast as a starting point, but update forecasts closer to the point of decision to improve accuracy. Delay committing to manual forecast changes whenever possible.
Step 9: Learn and Improve: Setting Goals and Applying Lessons for Better Forecasts
Continuous improvement is the name of the game. Companies that consistently measure forecast accuracy, analyze the causes of errors, and apply lessons learned to future forecasts will see ongoing improvements. This isn’t a one-time effort; it’s a continuous journey. Demand patterns are constantly evolving, requiring attention to new trends. Management should foster a culture of continuous improvement.
As new demand patterns emerge, integrate them into the model to keep forecasts accurate. Provide training opportunities for continuous education and knowledge gap filling. Recognize that not all product categories can be managed the same way. Set realistic forecast accuracy expectations for each category. Don’t jump to conclusions based on one data point, and avoid playing the blame game. Look at trends over time for a more accurate assessment.
Step 10: Adding Value: Enhance Your Forecasting with VAS
Identify a point person responsible for coordinating the entire Value Added Service (VAS) workflow. Map out inputs, processes, and outputs. Measure the effectiveness of each segment or layer and create accountability for each involved party (sales, marketing, finance, demand planners, category team, management, operations, etc.). Make metrics visible at each level and keep the process consistent over time regarding what you’re measuring.
Track the efficacy and efficiency of VAS. For efficacy, monitor the value added or destroyed at each step compared to the previous one. For efficiency, compare the added value with the time spent on the forecast. Apply reward recognition across different parties in the company contributing to forecasting. For instance, if a sales team’s forecast was consistently within X% of actual sales, they were considered “accurate.” Set initial tolerances for forecast variance to ensure success is attainable and tighten them over time. Recognition is more important than the reward’s monetary value. Involve all parties driving initial demand for SKUs directly or indirectly.
Continuous Improvement
Repeat steps 3 through 10 by tracking and capturing FAMs and bias for each party involved. Forecasting should be a process of continuous improvement, requiring diligent and disciplined effort. Following this process will help you consistently improve forecast accuracy over time. Stick with a winning process despite a few bumps in the road—it’s the path to success.
By implementing these strategies, you can harness the full potential of Manhattan Active Supply Chain Planning, ensuring your forecasts are precise, your inventory is optimized, and your business is poised for success.
How Manhattan Active® Supply Chain Planning Can Help
Manhattan Active Supply Chain Planning is designed to support and enhance your efforts in achieving forecast accuracy. Here’s how it can help:
- Advanced Analytics: Leverage AI and machine learning to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and improve forecast accuracy.
- Real-time Data Integration: Integrate data from various sources in real-time, ensuring your forecasts are based on the most current information.
- Customizable Dashboards: Create and publish detailed dashboards with FAMs, offering clear and actionable insights into your forecasting performance.
- Scenario Planning: Simulate different scenarios to understand potential impacts and refine your forecasts accordingly.
- Collaboration Tools: Facilitate better communication and collaboration among team members, ensuring everyone is aligned and working towards common goals.
- Automated Processes: Automate routine tasks, allowing your team to focus on more strategic activities.
- Continuous Learning: The system learns and adapts over time, continuously improving its forecasting capabilities.
Manhattan Active Supply Chain Planning, combined with proven best practices, can transform your forecasting process, making it more accurate, efficient, and aligned with your business goals. Embrace the future of supply chain planning and drive your company towards greater success with Manhattan Active Supply Chain Planning.
Deliver On Your Promise to Customers
Get in touch with the Manhattan team to see how we can help.
Unpack the Surging Need for Unified Supply Chain Planning
Explore the only solution on a microservice API, cloud-native platform, that simplifies planning by unifying demand forecasting, replenishment, and allocation.

Demand Forecasting
A hybrid approach to forecasting that seamlessly blends the power of proven statistical models with cutting-edge AI.
Replenishment
Seamlessly integrates AI-driven insights with real-time data to autonomously optimize inventory levels across all channels, ensuring the right products are always in the right place at the right time, without the need for manual intervention.
Allocation
Maximize sales opportunities, minimize stockouts, and optimize inventory across all locations and channels with unparalleled precision. Powered by cutting-edge AI and machine learning, our solution ensures your products are always in the right place at the right time.






