What is a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is essential supply chain software designed to optimize warehouse operations. Are you struggling with inefficient warehouse processes? A WMS streamlines inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and resource management, ensuring maximum efficiency in managing inbound and outbound logistics. This guide explores what a WMS is, its key functionalities, and why it's vital for effective supply chain management.
What is a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
What is Warehouse Management?
Warehouse management involves the use of systems and processes to oversee and control operations within a warehouse. The primary goal of warehouse management is to ensure that goods are received, stored, and shipped in the most efficient and cost-effective manner. Key functions include inventory management, order fulfillment, and optimizing the use of resources such as labor and equipment.
Omnichannel commerce technology advancements and post-pandemic consumer habits — the former being expedited by the latter — have increased the responsibility on distribution centers and warehouse management processes to adhere to expectations of modern supply chain capabilities. Consumers today can receive everything — from time-sensitive orders of groceries and medication to clothes and furniture — delivered to their front door with complete transparency of where a purchased item is and when it will arrive throughout the supply chain journey.
Other businesses and industries — such as B2B customers, wholesalers, manufacturing companies, etc.— as a result of the current supply chain landscape, also expect warehouse management to be agile and flexible with seamless order changes made possible from dock to truck, along with network-wide visibility, and optimized inventory capacity, storage, and slotting.
Warehouse management is vital to ensuring distribution operations run smoothly and optimally with processes in place that control and oversee labor, inventory, customer orders, picking, and loading in a warehouse or distribution center. To execute profitably and consistently on efficient warehouse management, leading to increased customer satisfaction and optimal supply chain logistics, organizations need the right warehouse management system (WMS) to bring it all together.
What is a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a software application designed to support and optimize warehouse or distribution center management. These systems facilitate the management of daily warehouse operations, including inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and resource management. The primary roles of a WMS are to manage inventory levels, orchestrate order fulfillment, and optimize all warehouse operations from inbound receipts to outbound shipping.
It is used by manufacturers, distributors, and merchants of all sizes to drive the utmost efficient labor and fulfillment capabilities and to maximize inventory storage. In short, it optimizes warehouse inventory management software and operational capabilities.
WMS is a vital component for any national or global supply chain operation as it keeps track of every single product item that goes in and out of distribution. A modern WMS provides full enterprise-wide visibility of inventory and complete visibility of a product’s journey throughout the distribution cycle. 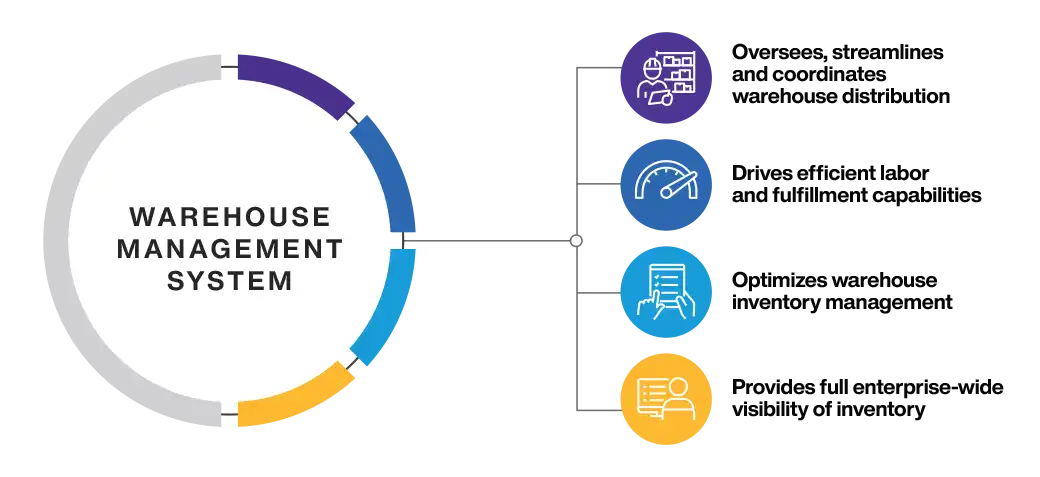
A Brief History of WMS
Historically, warehouse management involved manual tallying. The advent of computers in the 1970s and the barcode in 1974 revolutionized WMS. Barcodes reduced human error, and warehouses became more efficient. By the 21st century, advancements in computing increased WMS agility and scalability, meeting global distribution needs. Key Takeaway: Technology has dramatically transformed warehouse management from manual processes to agile, scalable systems.
The push to cloud computing technologies was a game changer in the industry, first becoming mainstream with the launch of AWS in 2006. In roughly the mid 2010’s, cloud-native solutions started to gain traction, and supply chain commerce leaders have been upgrading and advancing their technology capabilities ever since.
In 2017 Manhattan launched Manhattan Active® Solutions — including Manhattan Active® Omni — the first cloud-native, evergreen, extensible foundation for supply chain commerce, and Manhattan Active® Warehouse Management.
The Role of WMS in Supply Chain Order Processing
A WMS plays an important role in supply chain order processing by optimizing the fulfillment of orders from the moment it arrives in the warehouse to the moment the order is placed on the dock for outbound transport movement. The right WMS ensures the correct order is received and stored in the optimal location for order inventory storage, picking, tracking, and fulfillment. Labor is managed and streamlined with automation for shipping and receiving tasks, optimized pick paths are charted for the shortest distance traveled, and inventory is tracked via barcode readers and radio frequency identification (RFID) tags for inventory update visibility.
The WMS then updates inventory management numbers to notify the enterprise resource planning (ERP) software system, which primarily oversees accounting, compliance, invoicing, procurement, and order management.
A TMS then enables users to manage transportation planning and execution through modeling, procurement, multi-modal support, fleet and carrier coordination, insights, and sustainable shipping capabilities.
When unified on a singular platform, enterprises can orchestrate in perfect symphony inbound and outbound logistics. This unification consolidates all distribution and transportation management in a unified cloud-native solution that continuously adapts and scales to business needs. 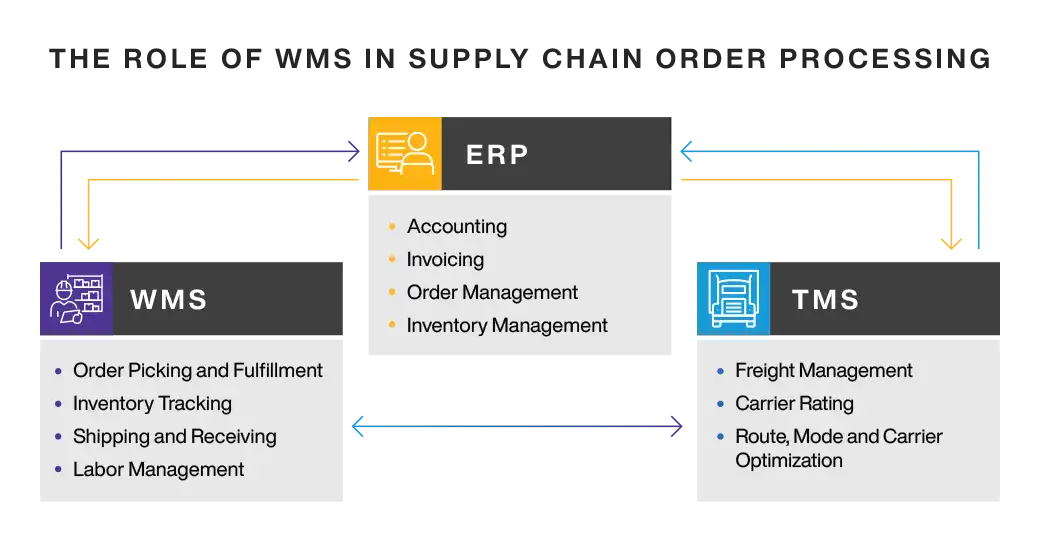
Significance of Implementing a WMS
Implementing a WMS boosts your supply chain by improving efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. When selecting a WMS implementation partner, consider the process: kickoff, design, build, preparation, testing, deployment, and ongoing support. Why is this important? A smooth implementation ensures you maximize the benefits of your WMS investment from day one.
In the modern supply chain and logistics world, having an implementation partner to guide you through the entire implementation process, and long after with upgrades and evergreen technology capabilities integrated as supply chain software improves, is vital to sustaining supply chain growth, providing the ability to change with industry and technology advancements. A modern WMS must also be agile, adaptable, and able to scale at an enterprise level to keep up with peaks and supply chain stresses that can be volatile due to a number of factors, such as geopolitical dynamics and disruptions.
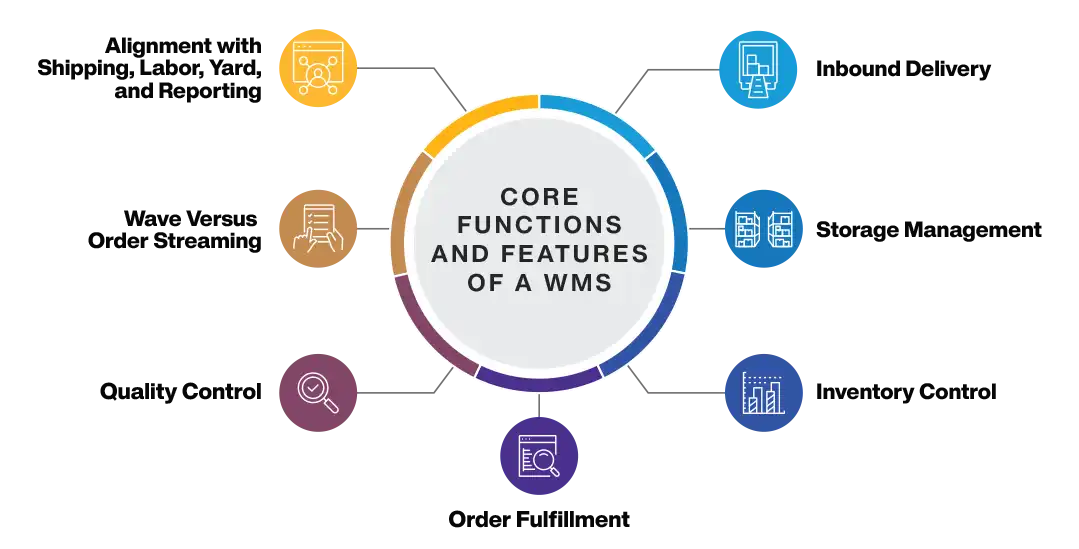
Core Functions of a Warehouse Management System
Inbound Delivery
Inbound delivery of product normally arrives at a facility from a supplier or third-party vendor for businesses who request the product to store for inventory management. In the case of manufacturers, its buying raw materials and having those arrive via inbound delivery to prepare for the next stage of distribution.
Inbound delivery is a vital piece of the supply chain puzzle as it is the first stage of production or distribution. If mismanaged, it can affect the rest of the supply chain process. WMS capabilities help optimize the inbound flow — especially if unified on a singular platform with other solutions such as TMS — by leveraging ordering and receiving to streamline the logging of inbound items, quality control measures during receiving, enterprise-wide visibility, transportation, and inventory management features.
Storage Management
Storage management features in WMS manage the space where inventory is placed in a warehouse or distribution center optimally, considering factors such as warehouse layout, high-priority, high-demand, or high-turnover product, pick paths, stacking and slotting of pallets, and more. There are multiple ways of storing inventory optimally, all depending on specific business needs.
The FIFO (First In, First Out) method of storing product refers to inventory that first comes in a warehouse being sold first to keep the flow of goods moving in one direction, through one end and out the other. The LIFO (Last In, First Out) method does the opposite, with the last order of inventory stored being the first batch out the door. Essentially, as long as the space is being utilized efficiently, both can be effective methods of storage management, depending on product and business needs. These two methods of storage are referred to as zoning methods, dividing a warehouse into zones to categorize product via zones. These methods can optimize space, reduce costs, and minimize distances traveled to retrieve an order placed.
Inventory Control
Inventory control features found in a WMS allow users to gain enterprise-wide control of inventory to ensure the correct amount of product is available to meet customer demand. Feature capabilities such as real-time visibility into product status, product aging, and
product batches, and advanced cycle counting help to maximize profits by meeting customer expectations of available product.
Real-time tracking inventory control capabilities provide up-to-date visibility for inventory levels to enable last minute order changes prior to shipment and accurate real-time inventory information. When integrated with forecasting and inventory optimization tools, inventory control capabilities within a WMS can create more efficient forecasting and replenishment strategies to optimize customer service and reduce out-of-stock or expired product.
See how KeHE Food Distributor took a fresh approach to inventory management.
Order Fulfillment
WMS order fulfillment features can complete the order fulfillment process for retail, wholesale, and direct demand by ensuring real-time alignment between orders and available inventory to fulfill orders on-time and accurately. Once an order arrives, order fulfillment processes sort the orders based on factors such as urgency, type of fulfillment, and customer need. The right resources are then allocated and workflows are streamlined for picking, packing, and shipping.
When unified with transportation management, WMS order fulfillment capabilities secure on-time deliveries without costly shipment upgrades and provide continuous transportation optimization to ensure trailers also ship as highly utilized as possible.
Learn more about Manhattan Active Warehouse Management’s Order Streaming.
Quality Control
Quality control is vital to WMS processes as it upholds rules and regulations to ensure products meet the quality standards of the end customer. Efficient quality control capabilities support quality testing and manage material holds, reducing the possibility of shipping defective products out. Effective quality control in WMS complies with regulatory standards, and leads to cost savings, reduction in waste, and improves customer satisfaction.
Wave Versus Order Streaming
Wave management in warehouse management is the process of grouping orders together for wave fulfillment based on similar or equal order characteristics such as shipment date, order priority, same items, warehouse zone, etc.
Order streaming optimizes utilization of resources to dynamically scale to accommodate warehouse or distribution center needs and constraints. Order Streaming technology, within Manhattan Active Warehouse Management, takes a more intelligent approach to orchestration logic by constantly ensuring real-time alignment between orders to fulfill available inventory. Manhattan Active WM is also the first and only data-driven warehouse management solution that knows how to learn and adjust orchestration logic in real time to maximize asset utilization.
Alignment With Shipping, Labor, Yard, and Reporting
Modern warehouse management solutions are built on a single platform, which opens the door to unification and flawless modern experiences.
A unified supply chain, with WMS, labor management, yard management, slotting optimization, and transportation management software all working together in a symbiotic cloud environment can unlock unprecedented supply chain agility, visibility and execution — all on a single device.
Learn more about continuous and collaborative planning across inventory, labor, distribution, and transportation.
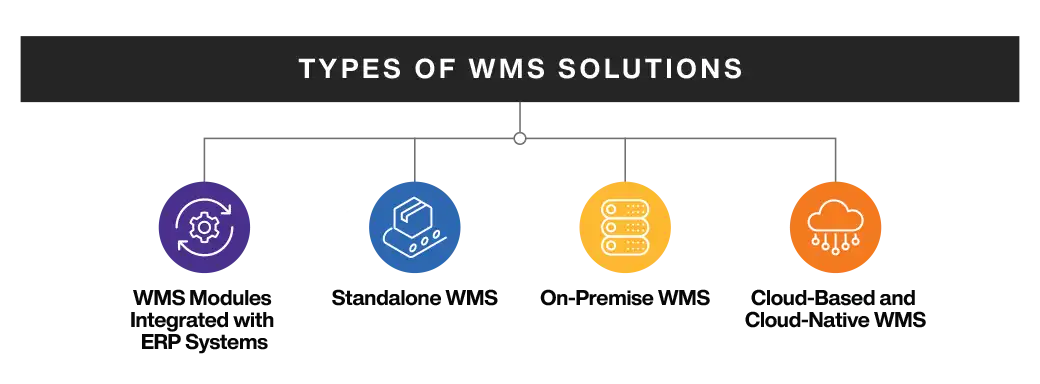
Types of WMS Solutions
There are various types of WMS solutions that serve specific purposes and feature different software capabilities. Each one can be leveraged to fulfill warehouse management requirements depending on the size of supply chain and organizational needs.
WMS Modules Integrated with ERP Systems
An integrated WMS module added on to existing ERP systems allows for tracking of orders to determine which type of order is providing the most profitability. With the integration of ERP systems tracking inventory and managing tasking for accounting and invoicing, and a WMS managing order picking, packing, shipping, and receiving, organizations can develop order fulfillment strategies based on synced inventory data from ERP and WMS.
Standalone WMS
A WMS standalone software is equipped with capabilities that are specific to warehouse management. Standalone WMS is ideal for small to medium size businesses who may not have the budgetary resources or business needs for further logistic services. The standalone WMS modules consist of best-of-breed capabilities for inventory management or distribution operations, including cycle counting, barcode scanning, picking, packing, slotting, and shipping.
On-Premise WMS
On-premise WMS is technology housed in a distribution center or warehouse on-site and managed by internal IT personal or resources. On-premise WMS software does no rely on internet connections and can be useful in areas where regional data restrictions and regulations are in place.
Cloud-Based and Cloud-Native WMS
Cloud-based WMS leverage the scalability of the internet to autonomously harness vast amounts of computing power and are available remotely via an internet connection. Conversely, “cloud-native” applications are born in the cloud, capitalize virtualization and containerization, and use APIs extensively. These differences make them significantly more scalable, dependable, and affordable.
The best cloud-native WMS solutions are built entirely with microservices or discrete functional components that eliminate the need to duplicate capabilities and data. Technology, such as Manhattan Active Warehouse Management, shares the same composable, microservices components. That means it never needs upgrading and is fully extensible, which allows companies to plug in their own innovation without impacting future updates, and provide seamless integration to other systems.
Cloud-native WMS solutions are scalable, automatically adding capacity to meet spikes in demand and then reducing it when needs lessen. Microservices architecture also seamlessly and continuously adds new innovations and capabilities over time. It is designed specifically and uniquely for the modern supply chain world.
The Five Key Features of WMS
Inventory Management
- Tracks the movement and storage of materials within a warehouse.
- Provides real-time visibility of inventory levels, locations, and statuses.
- Helps in maintaining accurate inventory records and minimizing stock discrepancies.
Order Management
- Facilitates order processing, picking, packing, and shipping.
- Ensures accurate and timely fulfillment of customer orders.
- Supports different order types, including retail, wholesale, and direct-to-consumer.
Labor Management
- Monitors and optimizes labor performance and productivity.
- Assigns tasks based on worker availability and skill sets.
- Provides tools for tracking and improving workforce efficiency.
Warehouse Optimization
- Uses algorithms to optimize warehouse layout and product placement.
- Reduces travel time and improves picking efficiency.
- Enhances overall warehouse throughput and productivity.
Integration With Automation
- Integrates with various types of automation, such as robotics, conveyors, and sortation systems.
- Facilitates seamless coordination between human and automated processes.
- Enhances the efficiency of automated material handling systems.
The Key Benefits of WMS
The key benefits of the best WMS systems available on the market include:
- Improved Efficiency- Automates and streamlines warehouse processes, reducing errors and saving time.
- Better Inventory Control- Provides accurate, real-time visibility into inventory levels and locations.
- Enhanced Scalability- Adapts to changes in demand and business requirements.
- Labor Optimization- Ensures optimal use of labor resources, improving productivity.
- Cost Savings- Reduces operational costs through improved efficiency and accuracy.
Advanced Features of Modern WMS
Automation, Robotics, and Integration
Modern WMS and future WMS features will continue to develop easier and more advanced automation, robotics, and integration capabilities. Modern automation and robotics WMS features are making the lives of workers easier through seamless synchronization of human and machine to simplify processes and save valuable time on warehouse management tasks, freeing the workforce up for more pressing issues to address.
Manhattan Active WM easily integrates with any advanced material handling equipment, such as sortation equipment, put walls, and automated storage and retrieval systems. It also communicates with the latest robotic solutions on the market. The Manhattan Automation Network makes it easy to onboard new automation technology by facilitating
collaboration between Manhattan and our industry-leading partners.
Use of IoT
Modern WMS utilizes IoT (internet-of-things) smart technologies to facilitate communications between systems and the cloud. This capability provides real-time data and its automation can be used to track and monitor processes including regulate and oversee storage temperatures and optimize storage, for example notifying warehouse managers when items are close to out-of-stock.
Application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning in WMS
AI is becoming more complex in its abilities to automate and simplify workflows, uncover hidden insights, and accelerate innovation for warehouse operations. AI is being leveraged in a variety of ways in modern WMS technology, including using autonomous robots to relocate and pick goods within or around the warehouse, GenAI assistants that can provide actionable support and answer any warehouse management solution-related questions through human-like chatbot interactions, simplified system configurations, and intelligent knowledgebases that enable informed decisions.
Manhattan is leveraging Large Language Model (LLM) AI to drive unprecedented transformations in business efficiency, decision-making, and innovation, arming businesses with the tools needed to rapidly evolve with dynamic market changes.
Learn more about how Manhattan Active® Platform is unleashing the potential of generative AI.
WES Inside WMS
A WES (warehouse execution system) enables synchronization and optimization of automated workflows and processes — such as robots for picking and sorting — for distribution. Omnichannel stresses and labor volatility in the modern supply chain landscape has made automation an increasingly essential function of warehouse workflows and WMS software with advanced WES and WMS coordination capabilities have become increasingly more vital for profitable and efficient warehouse and distribution center operations.
Manhattan has added automation to deliver complete command and control of the warehouse, with the industry’s first WES built into a WMS.
Learn more about this feature provides control of every aspect of the distribution center with automation that delivers complete orchestration of robotics and people.
Challenges and Considerations in WMS Implementation
There are a few challenges and considerations to take into account when implementing a WMS. Implementation usually takes around six to nine months until ready for go-live. Costs vary based on type of WMS and overall features and accommodations. Some WMS providers source third-party vendors for implementation services, while others may provide their own services for implementation and post-launch to ensure their WMS customers are getting the most out of their WMS software.
The phases of implementation when a WMS provider undergoes a partnership with its customer each come with their own challenges to address and business considerations to contemplate to determine the implementation services required of the project, based on business need. The steps of this process are as follows:

Phase 0 Sales Transition: This phase establishes initial project plan and objectives after the sale, including which hardware will be used, contract signing, training, and other sales transition requirements.
Phase 1 Design: Normally consists of a kickoff meeting where the provider and customer collaborate on which factor will lead to a successful implementation, the functional and interface design, and further training.
Phase 2 Build: After the environment in which the system will live in is ready to be tested, system configuration and unit testing take place, with integration development, knowledge transfer between teams, and end-user training to follow.
Phase 3 Prepare: Integration, volume, user acceptance, and end-user training occur, with mock conversion and a risk assessment that prepares the customer for possible challenges that may arise after go-live.
Phase 4 Deploy: Execution of conversion plan and go-live are now ready to occur. After go-live takes place post-implementation support is now given by the provider, including statistics and notifications for overseeing how the new software is performing, as well as where improvements can be made.
Phase 5 Support: The implementation portion of the project comes to a close, with a transition then to customer support that includes a post-project assessment and ongoing improvements when needed, ideally periodically until the customer undergoes an upgrade.
Significance of Implementing a WMS
Implementing a Warehouse Management System (WMS) is significant for businesses looking to optimize their warehouse operations and improve overall efficiency. Here are the key reasons why implementing a WMS is crucial:
Enhanced Inventory Management
Real-Time Visibility- A WMS provides real-time tracking of inventory levels, locations, and statuses, allowing for accurate and timely inventory management.
Reduced Stock Discrepancies- With precise inventory control, businesses can minimize discrepancies, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
Improved Order Fulfillment
Faster Processing- A WMS streamlines order processing, from picking to packing and shipping, ensuring faster fulfillment of customer orders.
Accuracy- Reduces errors in order fulfillment, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing returns.
Labor Optimization
Task Assignment- Optimizes the assignment of tasks based on worker availability, skills, and current workloads, improving labor productivity.
Performance Tracking- Monitors labor performance, providing insights to manage and improve workforce efficiency.
Operational Efficiency
Process Automation- Automates routine tasks such as inventory tracking and order processing, freeing up human resources for more strategic activities.
Warehouse Layout Optimization- Uses algorithms to optimize warehouse layout and product placement, reducing travel time and increasing picking efficiency.
Scalability and Flexibility
Adaptability- A WMS can scale with the growth of the business, adapting to changes in demand and business requirements.
Integration- Seamlessly integrates with other supply chain systems and automation technologies, ensuring unified and efficient operations.
Cost Reduction
Operational Costs- By improving efficiency and reducing errors, a WMS helps lower operational costs.
Inventory Costs- Optimized inventory management reduces holding costs and minimizes losses due to obsolescence or spoilage.
Data-Driven Insights
Analytics- Provides detailed analytics and reporting, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Continuous Improvement- Helps identify areas for improvement, driving continuous optimization of warehouse operations.
Enhanced Customer Service
Order Accuracy and Speed- Ensures accurate and timely order fulfillment, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Transparency- Provides customers with real-time information about their orders, enhancing trust and reliability.
Compliance and Traceability
Regulatory Compliance- Helps businesses comply with industry regulations by maintaining accurate records and providing traceability of goods.
Traceability- Ensures that all movements of goods are tracked, aiding in quality control and recall processes if necessary.
Competitive Advantage
Efficiency- A WMS provides a significant competitive advantage by enabling faster, more accurate, and cost-effective warehouse operations.
Customer Satisfaction- High levels of efficiency and accuracy translate into better customer experiences and increased loyalty.
Industry Use Cases for WMS
WMS can be a valuable asset for a variety of industries with industry specific warehouse and distribution management needs.
Consumer Goods
A WMS can accurately and efficiently execute distribution for Consumer Goods’ organizations from receiving to fulfillment, with solution capabilities to navigate industry-specific regulations, storage requirements, tracking requirements, labor challenges, and service-level agreements.
Consumer Goods Supply Chain Software
Food & Beverage
A WMS can provide the right temperature requirements for storage and movement of temperature-sensitive Food & Beverage goods. It can also provide tracking and tracing solution capabilities to ensure the correct quantity and quality of items are safely stored and transported, reducing the likelihood of shipped expired products.
Food and Beverage Supply Chain Software
Grocery
Grocery items are an essential human need and WMS solution capabilities can enable grocery products to arrive at their desired destination fast and without fail. Online grocery shopping is a common method of fulfillment placing relatively new stresses on supply chain networks. Distribution operations need the right solutions to fulfill grocery orders in a timely and efficient fashion. The right WMS capabilities can give distribution managers greater visibility and control with highly actionable, real-time operational data visualizations across every facility and integrated, direct communication with the workforce — effectively minimizing out-of-stocks (OOS) — and managing a changing labor force.
Grocery Supply Chain Software
Wholesale
Wholesalers face industry challenges — product, price, speed of delivery, sourcing, inventory, and fulfillment — compounded by inflation and labor shortages. The right WMS can process orders quickly and more efficiently with capabilities that streamline receiving, put away, picking, packing, and shipping while simultaneously enabling optimization of warehouse layout and operations.
Wholesale Supply Chain Software
Medical and Pharmaceutical
Medical and Pharmaceutical distribution and warehouse management capabilities can be life-saving. A WMS can meet challenges associated with industry needs — including temperature-sensitive shipment requirements, expiration dates, unpredictable demand, labor shortages, and changes in regulations — with both human and robotic counting, filling, and dispensing capabilities. The right WMS can ensure transparency and traceability across every level of every facility — enabling flow-through processing for products with a short shelf life, ensuring regulatory compliance, and accelerating delivery to the point of care.
Medical and Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Software
Retail
Direct-to-consumer fulfillment has placed new responsibilities on distribution centers and warehouses to provide inventory available for customer fulfillment at a multitude of points throughout the product journey. Omnichannel fulfillment strategies can allow retailers to ship product to wherever the customer desires, whether it be the nearest retail store or directly to the customer’s house. WMS combined with other retail omnichannel solutions can sync back-end supply chain operations with the front-end by unifying supply chain execution and store solutions, providing unprecedented control, visibility, and profitable outcomes.
Retail Supply Chain Software
Manufacturing
Manufacturing industry challenges such as quality control of raw materials, regulatory compliance, inventory management, and capacity constraints can provide stresses on warehouse management. A WMS can help solve these challenges through inventory control, managing picking and packing, and optimizing warehouse space. Integration WMS capabilities are also beneficial to manufacturers to connect to other systems with end-to-end visibility and connections between suppliers, customers, and third-party logistics services.
Manufacturing Supply Chain Software
Third-Party Logistic (3PL) Providers
Digital transformations — especially ecommerce and omnichannel commerce — have changed what customers expect from a 3PL provider. Warehouse capacity constraints or shortages can also effect a 3PLs ability to add new customers or meet peak demand surges. A WMS can provide agile and scalable management capabilities that help maximize space utilization and optimize fulfillment. It can also coordinate value-added services 3PLs provide — such as gift wrapping, personalization — without slowing down shipping times.
3PL Supply Chain Software
Government
The status quo can change at a moment’s notice for any federal government agency or military operation. When duty calls, the supply chain technology these organizations rely on must be ready to pivot or solve any crisis they might encounter. A best-of-breed WMS can utilize advanced algorithms to optimally orchestrate warehouse processes and synchronize work processes — elevating human performance, maximizing equipment utilization, and enhancing process visibility for government supply chain logistics. With Manhattan Warehouse Management, users can easily configure storage to be organization-specific or allow mixing of inventory across organizations within a single location, zone, etc., to optimize space.
Learn More
Manhattan’s WMS Solves Specific Industry Challenges
Manhattan’s WMS enables global distribution control of demand, supply, labor, and automation supply chain network-wide with industry-leading evergreen, extensible, cloud-native technology.
Bidfood
See how leading Dutch food service wholesaler Bidfood optimized its distribution network with track-and-trace and voice-picking features that enable Bidfood to drive faster and more efficient distribution throughout its supply chain network.
DHL
See how DHL improved agility for its warehouse operations and broke the upgrade cycle with Manhattan Active Warehouse Management and learn more about the benefits of going versionless, as well as how Manhattan’s successful partnership combines with DHL to provide better and quicker solutions for its customers.
Raia Drogasil
See how Raia Drogasil, the largest drugstore company in Latin America, optimized its warehouse management with Manhattan Active WM, enabling unified control of all DC operations, reduced time for receiving products, increased stock accuracy, and implemented total resource traceability.
Why Manhattan Active Warehouse Management is Best-in-Class
Manhattan Active Warehouse Management is an industry-leading enterprise-class warehouse management system (WMS) that unifies every aspect of distribution and never needs upgrading. It is a 16-time leader in Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Warehouse Management Systems and is recognized as a leading vendor to offer a 100% microservice cloud-native WMS.
Manhattan is trusted by top global retailers, national and international grocery chains, wholesale distributors, and consumer goods and pharmaceutical manufacturers for their planning, execution distribution, and logistics operations.
Its differentiating solution features include:
Slotting Optimization
Determines the best locations to slot your inventory, increases workforce efficiency, shortens order fulfillment cycles, and maximizes throughput. It also improves customer service by strategically grouping items for fulfillment and updating placement recommendations based on trends and new product demand.
Unified Control
Delivers access to detailed, real-time data visualizations with actionable insights that include a network-wide summary of performance across all distribution nodes and hubs throughout the organization. Unified control provides complete command and control of the distribution network from the highest levels to the smallest data elements.
Order Streaming
Delivers a more intelligent approach to orchestration logic by constantly ensuring real-time alignment between orders to fulfill available inventory. Manhattan Active WM is also the first and only data-driven warehouse management solution that knows how to learn and adjust orchestration logic in real time to maximize asset utilization.
WES Inside WMS
Manhattan Active WM features the first ever WES inside of WMS, enabling users to coordinate human and machine effortlessly. Designed to redefine warehouse management for the modern, automated era, this solution feature is not only vendor- and equipment-agnostic but also designed to grow with your automation needs seamlessly. This unmatched flexibility allows users to incorporate new technologies, switch vendors, or scale your operations without restrictions.
Warehouse Management Challenges Solve by Manhattan Active® Warehouse Management
Manhattan Active WM was built with specific solution feature capabilities to solve specific warehouse management challenges. Some challenges the solution solves include:
- Integrating and orchestrating warehouse management systems (WMS) and warehouse execution systems (WES) with warehouse control systems (WCS).
- Fulfillment of smaller orders, SKU proliferation, volatile demand, and shorter order cycle times that require nonstop warehouse space optimization.
- Access to detailed real-time data visualizations with the ability to take action in a single tool, whether in the office or on the floor.
- Maximizing trailer utilization and getting orders to the dock ahead of the carrier cut-off times and promised service commitments.
- Orchestrating resources and orders across retail, wholesale, and direct fulfillment workflows.
- Planning for the right amount of labor to continuously harmonize fluctuating priorities, inventories, and capacity.
- Eliminating the execution barriers of legacy distribution systems by unifying and orchestrating work seamlessly and simultaneously across both man and machine.
Customer Benefits Achieved With Manhattan Active® Warehouse Management
Virginia ABC now has end-to-end visibility of every order, which has sparked record throughput, even during peak season.
Skechers achieved enhanced operational efficiency, agility, and accuracy, enabling the retailer to effectively manage growth and deliver exceptional customer experiences worldwide.
New Balance greatly enhanced efficiency with Manhattan's automated capabilities, improved accuracy, saved precious time by eliminating the need to open boxes to count items with RFID, and increased customer satisfaction through new services and programs with Manhattan.
Warehouse Management System FAQs
A warehouse management system (WMS) is a supply chain software solution that oversees, streamlines, and coordinates every aspect of distribution in a warehouse or distribution center.
The four types of warehouse management systems are:
- WMS Modules Integrated with ERP Systems
- Standalone WMS
- On-Premise WMS
- Cloud-based or cloud-native WMS
A WMS is built to oversee and manage all warehouse activity, whereas an ERP is made to automate business processes — including human resources, customer relationships, inventory management, finance management, and procurement — for an entire organization’s enterprise.
A WMS is used by manufacturers, distributors, and merchants of all sizes to drive the utmost efficient labor and fulfillment capabilities and to maximize inventory storage in a warehouse or distribution center. Supply chain leaders in various industries — including manufacturing, wholesale, food and beverage, grocery, medical and pharmaceutical, third-party logistics providers, consumer goods, retail, and government — need a WMS to execute on distribution efficiently, profitably, and sustainably.
Modern WMS solutions are built on a single platform, which opens the door to unification and flawless modern experiences.
A unified supply chain, with WMS, labor management, slotting optimization, and transportation management software all working together in a symbiotic cloud environment can unlock unprecedented supply chain agility, visibility, and execution — all on a single device.
Manhattan Active® Supply Chain execution brings our WMS and TMS capabilities together to form end-to-end supply chain optimization, visibility and a level of execution never before seen and Manhattan Active® Supply Chain Planning provides continuous and collaborative planning across inventory, labor, distribution, and transportation.
Supply Chain Commerce Solutions
Manhattan offers a complete breadth of solutions that when unified, provides total coverage for your supply chain commerce needs.
Deliver On Your Promise to Customers
Get in touch with the Manhattan team to see how we can help.

17X WMS Magic Quadrant Leader
Recognized as a leader for the 17th time by Gartner, Manhattan is the only vendor in the Leader Quadrant to offer a 100% microservice cloud-native WMS.
WMS Related Articles
State of Warehouse Operations Report
Discover insights from 2,000 supply chain professionals about the current state of warehouse operations in this comprehensive research report.
Read ReportVirginia ABC Toasts New Distribution Center Capabilities With Manhattan
Discover how Virginia ABC transformed its operations with a state-of-the-art distribution center powered by Manhattan Active Warehouse Management.
Learn More









